一、数据获取
以下为数据获取的完整代码,直接使用 get 请求数据,网站只需验证正确的 User-Agent。同时在 JobSpider 中初步解析整理数据,使用 BeautifulSoup + CSS 解析数据,使用正则表达式整理数据完善字段。具体的解析逻辑参考网页源码。根据网页内容共获取职位标题、职位属性、职位描述、工资、福利、公司名称、公司属性、公司具体信息七个字段。获取后在将一些包含多种信息的字段分成多个字段。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
爬取 51Job-深圳-数据分析 招聘职位数据
"""
import re
import time
import urllib
import pandas as pd
import requests as rq
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
class JobSpider():
'''Get job data in 51Job with specific keyword and city.'''
def __init__(self, city, keyword, pages):
''' --------------- Init Params ------------------
city: str in ('北京', '上海', '广州', '深圳')
keyword: search keyword
pages: get how many pages
'''
cdict = {'北京': '010000', '上海': '020000', '广州': '030200', '深圳': '040000'}
self.city = cdict[city]
self.keyword = urllib.parse.quote(keyword).replace('%', '%25')
self.pages = pages
self.url = f'https://search.51job.com/list/{self.city},000000,0000,00,9,99,{self.keyword}'+',2,{0}.html?'
self.headers = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/73.0.3683.86 Safari/537.36'}
def get_job_links(self, page):
'''Get all job href in one page'''
res = rq.get(self.url.format(page), headers=self.headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(res.text, 'lxml')
tags = soup.find_all('p', {'class': 't1'})
get_href = lambda tag: re.compile('href="(.*?)"').findall(str(tag))[0]
links = [get_href(tag) for tag in tags]
return links
def get_one_job(self, link):
'''Parse a single job details'''
res = rq.get(link, headers=self.headers)
res.encoding = 'gbk'
html = res.text.replace('\n', '')
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
keys = ['job_title', 'job_attribute', 'job_description',
'wage', 'welfare',
'company', 'company_attribute', 'compny_details']
job = dict.fromkeys(keys, None)
job[keys[0]] = soup.select('div.tHeader.tHjob > div > div.cn > h1')[0].text
job[keys[1]] = soup.select('div.cn > p.msg.ltype')[0].text.replace('\xa0', '').split('|')
job[keys[2]] = re.compile('<div class="bmsg job_msg inbox">(.*?)<div class="mt10">').findall(html)[0]
job[keys[3]] = soup.select('div.tHeader.tHjob > div > div.cn > strong')[0].text
job[keys[4]] = [w.text for w in soup.find_all('span', {'class': 'sp4'})]
job[keys[5]] = soup.select('div.com_msg > a > p')[0].text
job[keys[6]] = [w.text.replace('\n', '') for w in soup.find_all('p', {'class': 'at'})]
job[keys[7]] = soup.select('div.tCompany_main > div:nth-child(2) > div')[0].text.replace('\xa0', '')
return job
def parse_dict(self, job):
'''Unpack stacked job details'''
keys = list(job.keys())
fields = [
'job_title',
'location', 'experience', 'education', 'hire_num', 'release_date',
'job_description',
'wage',
'welfare',
'company',
'company_type', 'company_size', 'business_field',
'company_description'
]
def get_element(i, lst):
try:
r = lst[i]
# except IndexError:
except:
r = None
return r
new_job = dict.fromkeys(fields)
new_job[fields[0]] = job[keys[0]]
for i in range(5):
new_job[fields[i+1]] = get_element(i, job[keys[1]])
new_job[fields[6]] = re.sub('<[^<]+?>', '', job[keys[2]]).strip()
new_job[fields[7]] = job[keys[3]]
new_job[fields[8]] = '|'.join(job[keys[4]])
new_job[fields[9]] = job[keys[5]]
for i in range(3):
new_job[fields[i+10]] = get_element(i, job[keys[6]])
new_job[fields[13]] = job[keys[7]]
return new_job
def main(self, start=1, delay=1):
'''Main function'''
for page in range(start, self.pages+1):
links = self.get_job_links(page)
job_list = []
for link in links:
try:
job = self.get_one_job(link)
new_job = self.parse_dict(job)
job_list.append(new_job)
print('\t' + link)
except:
print('[ERROR]' + link)
continue
time.sleep(delay)
pd.DataFrame(job_list).to_csv(f'page{page}.csv', index=False)
print(f'>>> Saved page{page}.csv')
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
if __name__ == "__main__":
# get data
# 由于 51Job 直接搜索会模糊匹配,只取前 24 页跟关键词相关性高的内容
pages = 24
js = JobSpider('深圳', '数据', pages)
js.main(1)
# join csv
jobs = pd.read_csv('page1.csv')
for i in range(1, pages):
df = pd.read_csv(f'page{i+1}.csv')
jobs = jobs.append(df)
jobs.to_csv('raw.csv', index=False)
# generate profile report
import pandas_profiling
profile = pandas_profiling.ProfileReport(jobs)
profile.to_file('profile.html')
二、数据清洗
根据不同字段的性质进行不同的清洗。例如工作描述,公司描述等字段,主要用作词频统计,不需要特别清洗。对于分类变量,需要统一取值并排除异常值,例如工作地点变量。对于连续变量,例如工资,需要转为数值型。对于时间戳,需要统一格式。以下为部分字段的示例。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# location 字段:统一取值,删除非深圳的职位
def unify_value(value, level1, level2=[]):
# 当 level1 中的匹配目标包含 level2 中的字符,则需要使用两个 level
for i1 in level1:
if i1 in value:
return i1
for i2 in level2:
if i2 in value:
return i2
# 失配取 None
return None
regions = [
'南山区', '福田区', '龙岗区', '宝安区', '龙华新区',
'罗湖区', '光明新区', '坪山区', '盐田区', '大鹏新区'
]
df[keys[1]] = df[keys[1]].apply(unify_value, level1=regions, level2=['深圳'])
df.drop(np.where(df[keys[1]].isna())[0], axis=0, inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True, drop=True)
# 大部分字段类似,主要使用 unify_value 函数
1
2
3
# 发布日期:简化取值,异常值取空值
df[keys[5]] = ['2021-' + v.replace('发布', '') if '发布' in str(v)
else None for v in df[keys[5]]]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 工资:转成数值元组,效果:1-1.5万/月 --> (10, 15)
def string_replace(string, dct):
for k, v in dct.items():
string = string.replace(k, v)
return string
rpl_dict = {'/': '-', '年': '12', '月': '1', '千': '-3', '万': '-4'}
df[keys[7]] = [string_replace(str(v), rpl_dict).split('-') for v in df[keys[7]]]
def get_tuple(lst):
if len(lst) == 4:
t1 = float(lst[0]) * 10 ** float(lst[2]) / float(lst[3])
t2 = float(lst[1]) * 10 ** float(lst[2]) / float(lst[3])
return (int(t1/1000), int(t2/1000))
df[keys[7]] = df[keys[7]].apply(get_tuple)
# 增加字段,将上面的元组拆了
df['wage_low'] = [w[0] if w else None for w in df['wage']]
df['wage_high'] = [w[1] if w else None for w in df['wage']]
最终结果如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
RangeIndex: 1116 entries, 0 to 1115
Data columns (total 16 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 job_title 1116 non-null object
1 location 1116 non-null object
2 experience 1010 non-null object
3 education 982 non-null object
4 hire_num 982 non-null object
5 release_date 982 non-null object
6 job_description 1116 non-null object
7 wage 1054 non-null object
8 welfare 900 non-null object
9 company 1116 non-null object
10 company_type 1116 non-null object
11 company_size 1062 non-null object
12 business_field 1116 non-null object
13 company_description 1116 non-null object
14 wage_low 1054 non-null float64
15 wage_high 1054 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(2), object(14)
memory usage: 139.6+ KB
三、数据可视化
可视化主要涉及分类字段的分布以及数值变量的分组聚合运算,逻辑并不复杂,在 Tableau 中可以很容易地绘图。对于行业领域和福利待遇两个字段,由于是嵌套列表的形式,将其转化为字符串列表再再 Tableau 中绘制词云图。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 行业领域
fields = '/'.join(
df.business_field.map(
lambda x: x.strip()
).map(
lambda x: x.replace(' ', '/')
)
)
pd.DataFrame({'行业': fields.split('/')}).to_csv('business_fields.csv')
# 福利待遇
welfare = '|'.join(df.welfare[-(df.welfare.isna())])
pd.DataFrame({'福利': welfare.split('|')}).to_csv('welfare.csv', index=False)
对于岗位描述字段,在 python 中进行分词。由于较多空泛的词组,这里使用正则表达式获取英文字符(表示技术栈),再进行词云可视化。具体操作如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# jieba 分词,非全模式分词
split_list = jieba.cut(str(' '.join(df.job_description)), cut_all=False)
text = list(split_list)
# 用正则匹配所有英文词组
uniq_words = pd.Series(text).unique()
eng_words = re.compile(r'[a-zA-Z]+?\|').findall('|'.join(uniq_words))
# 删除刚刚插入的辅助符号 “|”
eng_words = [v.replace('|', '') for v in eng_words]
# 去除上面 text 列表中的中文项(使用布尔型索引)
text = pd.Series(text)[pd.Series(text).map(lambda x: x in eng_words)]
# 增加其他停止词
stopwords = set(list(string.printable)) # 去除单个字符
stop_list = ['OR', 'with', 'ability', 'to', 'HR', 'on', 'including',
'the', 'have', 'other', 'of', 'be', 'at', 'our', 'as', 'related',
'and', 'year', 'Good', 'will', 'partner', 'you', 'technical', 'nbsp']
for s in stop_list:
stopwords.add(s)
# 绘制词云
wc = WordCloud(
width=1920, height=1080,
background_color='#1a1a1a',
font_path = './fonts/consola.ttf', max_font_size=400,
stopwords=stopwords,
random_state=50
)
wc.generate_from_text(' '.join(text))
plt.imshow(wc)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
四、分析报告
公司类型 | 公司规模 | 学历要求 | 经验要求
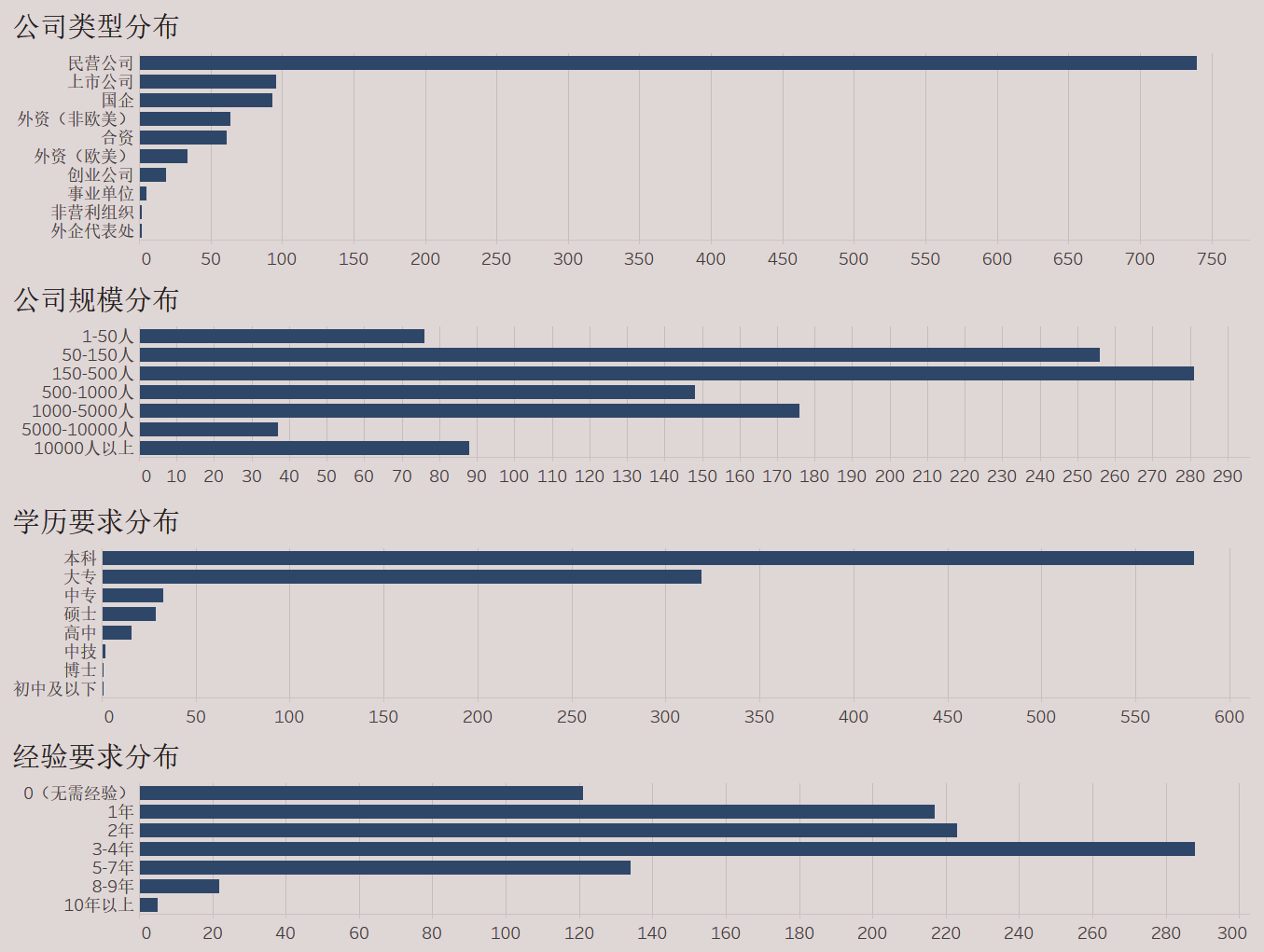
行业领域(一个职位对应多个领域)

福利待遇(一个职位对应多种福利)

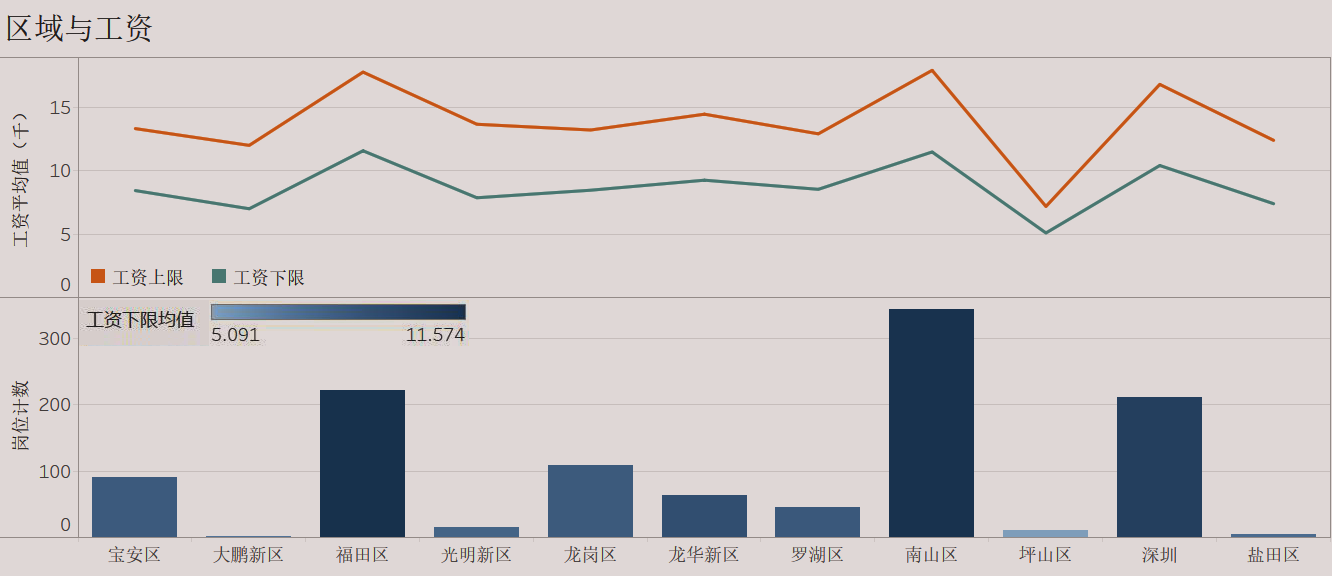
不同区域的工资均值以及职位数量
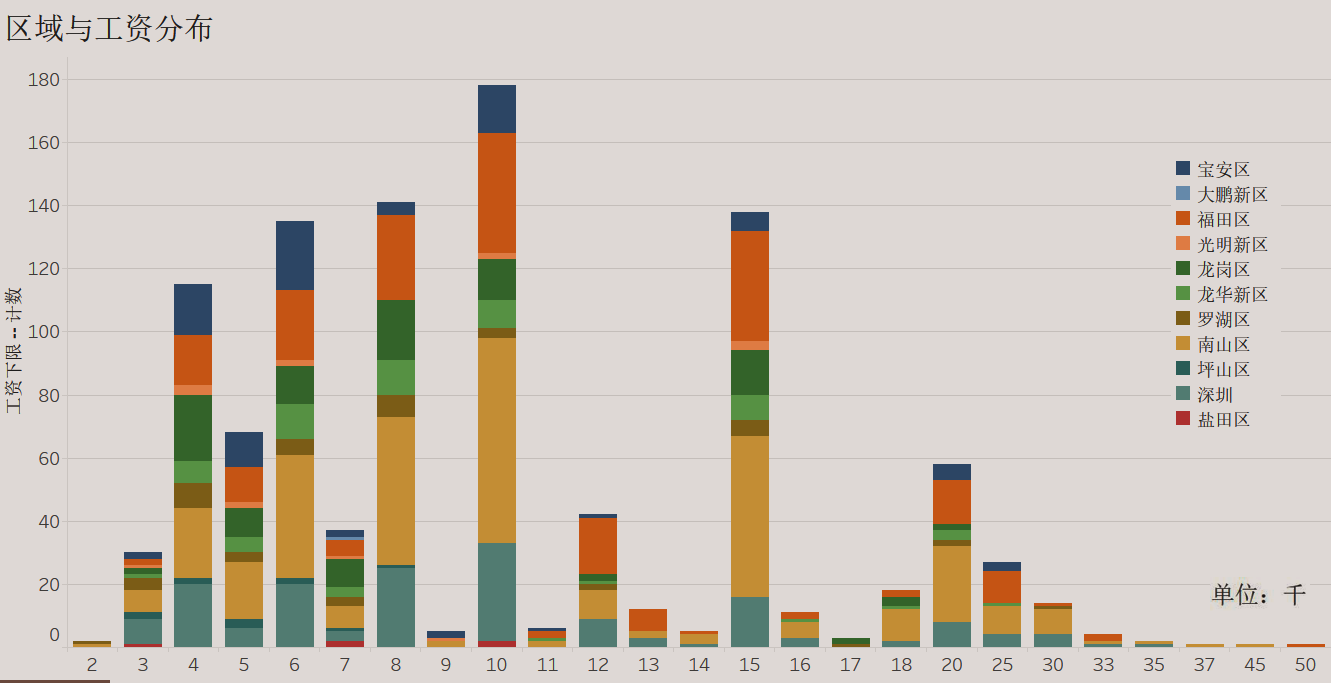
工资的具体分布(工资下限)
技能要求(提取自工作描述)
